The interplay of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) with surgery is revolutionizing healthcare for the unprecedented level of precision, efficiency, and care for the patient. Day by day, these technologies are revolutionizing the landscape of surgical procedures, from preoperative planning to postoperative care, and reshaping the roles of surgeons and healthcare providers.
This article discusses how the world of surgery is being revolutionized by AI and robotics and what the future of this dynamic profession may look like.
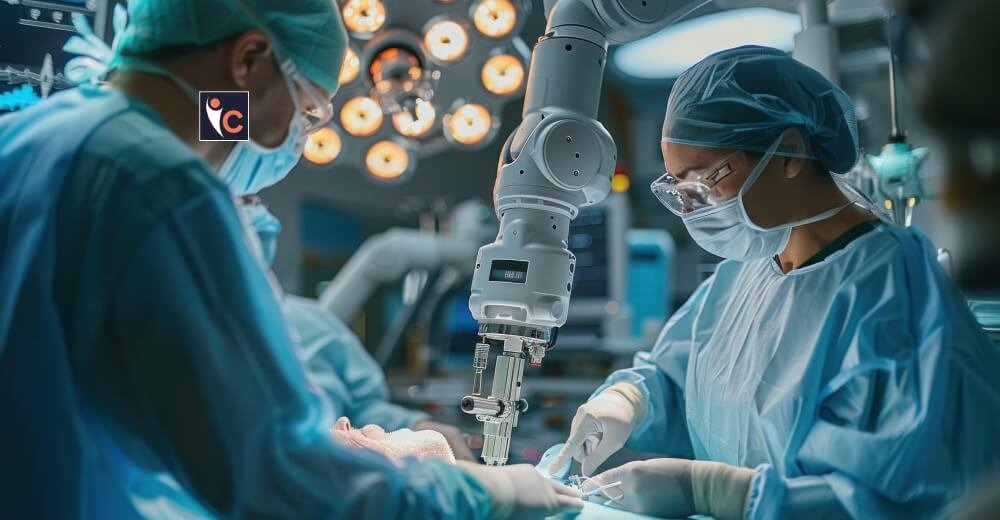
Precision and Accuracy Through Robotics
The hallmark of minimally invasive surgery is currently robotic surgery systems such as the da Vinci Surgical System. The systems allow the surgeons to perform complex procedures using a small incision, and the high-definition 3D images and robotic arms control the movements and transform the human movements into minute actions. Unlike the human hands, the robotic arms eliminate tremor and are more dexterous enabling skilled maneuverability to small areas like the brain or heart.
The precision of robotics limits the damage of neighboring tissues leading to less blood loss, minute scarring, and faster recovery. As in the case of prostatectomies, the rate of complications and improved functional outcomes with robotic systems have been lower as compared to conventional open surgery. With the further development of robotic technology, systems become more compact, the cost-effective and flexible, and are applied even to smaller hospitals and in a wider range of specialties including orthopedics and gynecology.
AI-Powered Decision Support
AI is improving surgical capability by providing evidence-based information at every stage of the process of surgery. During the preoperative planning, AI algorithms are used to scan medical images, such as MRIs or CT scans, and create accurate 3D models of a patient anatomy. Such models help surgeons to practice procedures, identify possible risks, and tailor interventions according to the particular patients. As an example, AI is able to detect the smallest abnormalities in scans, which may not even be noticed by human eyes, leading to increased diagnostic accuracy.
AI is a real-time assistant in surgery. Machine learning algorithms used in training on huge volumes of surgical videos can identify patterns and advise, for example, to recognize important structures like nerves or blood vessels. In other instances, AI systems warn surgeons of possible mistakes, thereby improving safety. Postoperative AI systems follow the healing of patients through monitoring of vital signs and forecasting complications such as infections, allowing early interventions.
Autonomous and Semi-Autonomous Surgery
The future of surgical innovation is autonomous and semi-autonomous systems. Fully autonomous surgery, where robots conduct surgeries without a human hand, is experimental, but semi-autonomous systems are catching on. These systems perform repetitive maneuvers, like suturing or cutting bone, with surgeon oversight, allowing human expertise to be reserved for higher-level decisions.
Improving Surgical Training
Robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the training of surgeons as well. AI-powered virtual reality (VR) platforms simulate operating rooms where the trainees may practice procedures in a safe environment. The simulations adapt to the ability of the user and provide individual feedback to accelerate the learning process. Robotic systems have also enhanced training through recording of the movement in surgery where beginners are in a position to learn and imitate the expert techniques.
This technology paves the way to quality training particularly in the situations in which resources are scarce. For instance, cloud-based VR platforms allow surgeons in rural locations to join forces with world experts, closing expertise gaps and enhancing global surgical standards.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While promising, AI and robotics in surgery are faced with significant challenges. They are expensive to access, and this is particularly so in poor regions, thus exacerbating healthcare inequalities. Incompatibility among proprietary systems renders it challenging to integrate into existing hospital practice. Also, reliance on AI raises potential concerns about data privacy, algorithmic bias, and over-reliance on technology, which, subsequently, may erode surgeons’ hand skills.
There are ethical concerns afoot. Who is responsible in the case of AI-generated error—the surgeon, the hospital, or the tech provider? How can patients give informed consent when AI algorithms are not transparent? Regulatory bodies like the FDA are adapting to deal with these challenges, but international standardization is still out of reach.
The Future of Surgery
In the future, the integration of AI and robotics is likely to result in completely integrated “smart” operating rooms. The rooms will integrate AI diagnostics, robot accuracy, and real-time data processing to achieve an optimal surgery aspect. IoT devices and wearable sensors may enable patients to be continuously monitored, sending their data into AI platforms to modify surgical plans dynamically.
Personalized medicine will be assisted. AI will analyze genetic and lifestyle data to recommend tailored surgical procedures, while implants 3D-printed with robotic precision will conform to the individual anatomy of each patient. And telesurgery, whereby physicians operate from afar through robotic grids, may bring specialist treatment to underserved populations, provided connectivity is addressed.